Regulations for Underground Power Installation In Sydney
Discover the intricate web of regulations governing underground power installations in Sydney. This comprehensive guide breaks down complex rules, offering clarity and insights for homeowners and contractors alike.
Did you know? Every year in Australia, thousands of electrical incidents occur, some resulting in serious injury or even death.
Strict regulations are crucial in Sydney to ensure the safety and legality of electrical work, particularly for complex jobs like underground power installations. These regulations outline safe practices for installation, materials, and electrician qualifications.
They not only protect residents from electrical hazards but also ensure installations comply with relevant building codes.
Regulation 1: Compliance with Australian Standards
Adherence to AS/NZS 3000 standards is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency in electrical installations. These standards, known as the Australian/New Zealand Wiring Rules, govern the installation process, ensuring that all electrical work is carried out safely.
Safety and Efficiency
Compliance with the AS/NZS 3000 standards, including the Electricity Safety Act 1998, is vital for the safety of electrical installations. Underground power cables and electrical equipment must be installed in accordance with these standards to prevent hazards.
The installation work must be carried out by licensed electrical professionals, ensuring all electrical wiring and connections meet the required depth installation for safety and efficiency.
Impact on Construction Demolition Sites
On construction demolition sites, the installation of underground electrical systems, including underground power installation, must ensure that power cables are protected. Electrical services and power installation work carried out on these sites must comply with general regulations.
Proper risk assessment and adherence to the Wiring Rules are essential to avoid common pitfalls.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Common pitfalls in electrical installation work include improper installation of underground power cables and failure to comply with local government regulations. To avoid these, ensure that the work is installed in accordance with AS/NZS 3000 and communicate clearly with your local authority.
Electrical cables less than high voltage should be handled by licensed professionals, and testing electrical systems should be completed within 20 business days.
Regulation 2: Proper Planning and Permits
Proper planning and obtaining necessary permits are crucial for any electrical project. These steps ensure compliance with regulations and safety standards.
Planning and Permits
Thorough planning must be done to install underground power and other electrical installations in accordance with AS/NZS 3000. The installation process involves securing approvals from your local authorities and ensuring that all work carried out meets general regulations.
Securing Approvals
To secure permits, submit detailed plans of your underground electrical work, including cable installation, to local authorities. Permits must be provided within 20 business days.
The depth of the underground cables’ installation must align with the Zealand Wiring Rules and the Electricity Safety Act.
Consequences of Neglect
Neglecting permits can lead to severe consequences, such as fines or project delays. Electrical connections, including consumer mains and sub mains subcircuits, must ensure compliance.
Installing underground wires or power lines without approval risks safety and interferes with the underground network. The main switchboard and any electrical service must only be installed by a licensed electrical professional.
Testing electrical systems and flexible cords must comply with the certificate compliance requirements set out for electricity safety in your area.
Regulation 3: Depth and Routing Requirements
Proper depth and routing of underground cables are vital for safety and functionality in electrical installations.
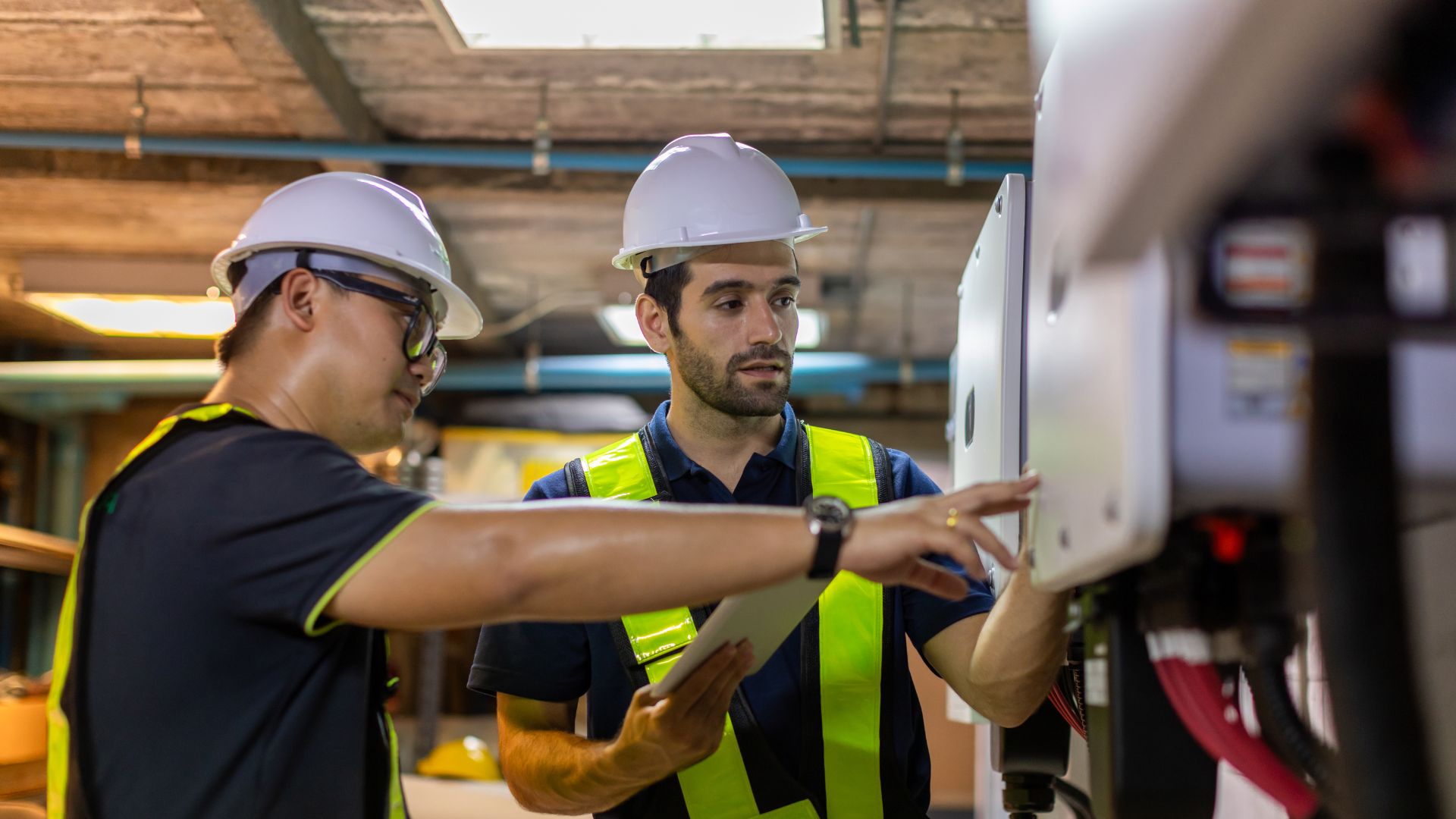

Required Depth for Underground Cables
Underground cables must be installed at a depth specified by AS/NZS 3000 standards. Typically, low-voltage power cables should be buried at least 600mm below the surface ground.
Use flexible plain conduit, complying with AS 2053, on the pole and within 1000mm of the base. This ensures protection from external damage and interference.
Routing Considerations
When planning the routing of cables underground, it is crucial to avoid existing utilities such as water pipes, gas lines, and telecommunications. Performing a thorough underground service check helps prevent disruptions and potential hazards.
Mapping the underground network accurately ensures cables are laid out in electrical systems safely and efficiently.
Tips for Compliance and Aesthetics
- Consult Local Authorities: Before starting the installation process, consult with your local government to understand specific regulations in your area.
- Use Licensed Professionals: Ensure that the work is carried out by a licensed electrical contractor to meet the Zealand Wiring Rules.
- Plan for Aesthetics: Consider using steel tubes or conduits to protect cables while maintaining landscape aesthetics. Flexible cords should be used where appropriate to allow for natural movement without damage.
- Documentation: Keep detailed records of the cable installation, including depth and routing, to assist in future maintenance and compliance checks.
Regulation 4: Use of Approved Materials
Using certified materials in electrical installations is crucial for ensuring safety and longevity.
Significance of Certified Materials
Certified materials meet stringent quality standards, ensuring they perform reliably under various conditions. Using these materials reduces the risk of failures and enhances safety, complying with regulations like AS/NZS 3000.
Common Approved Materials
- PVC and XLPE Insulated Cables: These are commonly used for underground power installations due to their durability and resistance to moisture.
- Steel Conduits: Provide protection against physical damage.
- Heat-Shrink Tubing: Ensures secure electrical connections and insulation.
- UV-Stabilised Materials: For any surface components exposed to sunlight.
Impact on Longevity and Safety
Quality materials resist environmental stressors, such as moisture and temperature fluctuations, ensuring the integrity of the underground network. This leads to fewer maintenance issues and prolongs the lifespan of the installation.
In addition, using approved materials minimises the risk of electrical faults, contributing to overall electricity safety and compliance with the Safety Act.
Regulation 5: Professional Installation and Inspection
Professional installation by certified electricians is essential for safe and compliant electrical systems.
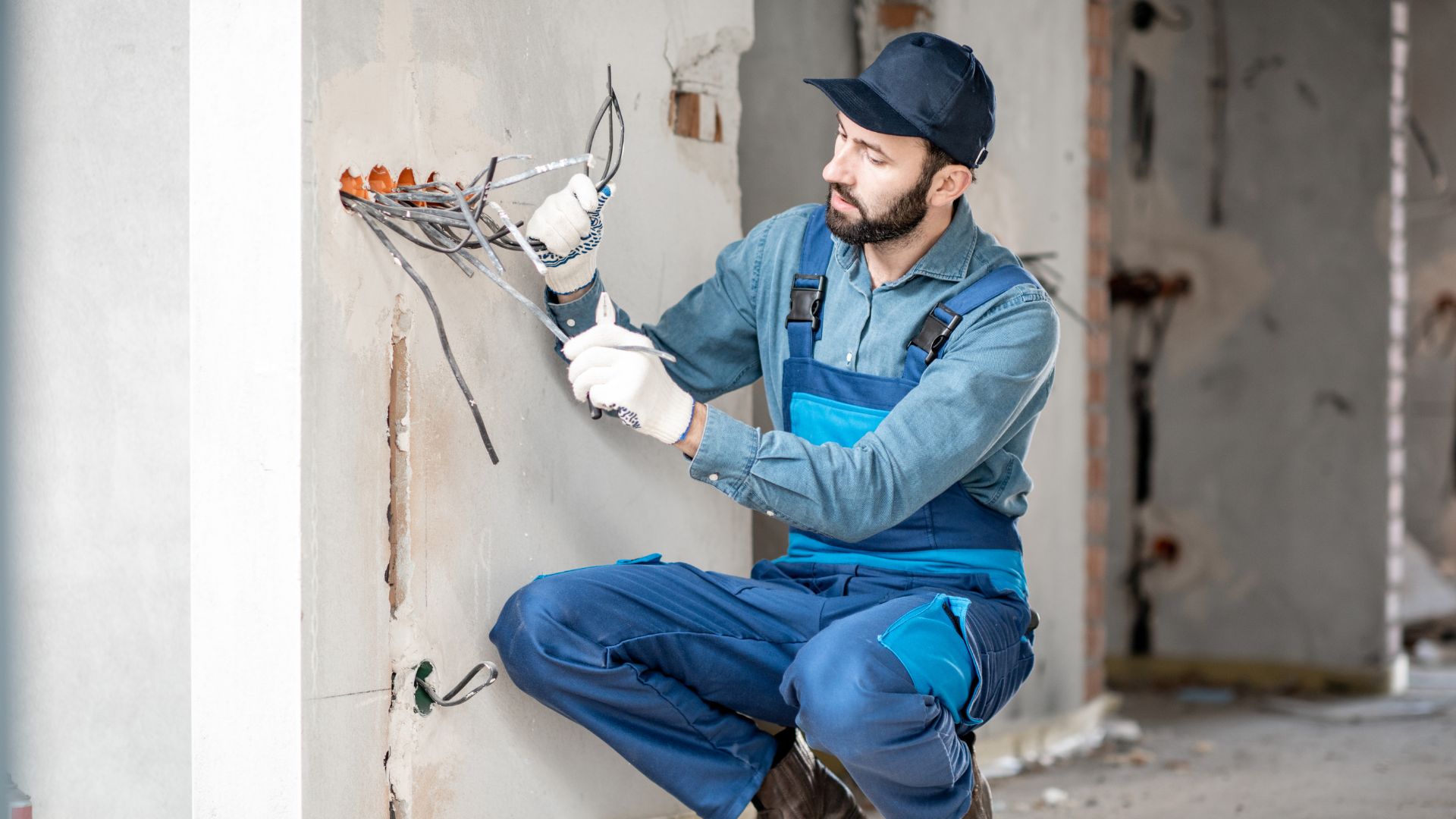

Need for Professional Installation
Certified electricians ensure installations meet AS/NZS 3000 standards, reducing the risk of electrical faults and hazards. Their expertise guarantees that the installation process adheres to safety regulations and technical requirements.
Inspection Process
Inspections verify that all work carried out complies with regulations. Inspectors check electrical connections, depth installation, and cable routing to ensure adherence to safety standards. This process is crucial for identifying and rectifying potential issues.
Common Inspection Failures
- Improper Cable Depth: Ensure cables are buried at the correct depth to prevent damage.
- Poor Connections: Use quality connectors and follow wiring rules to avoid loose connections.
- Inadequate Documentation: Maintain detailed records of the installation for future reference.
To prevent these failures, engage licensed professionals and conduct regular training on compliance standards. Regular inspections help maintain safety and efficiency in your underground network.
Regulation 6: Safety Measures and Signage
Implementing safety measures during and after installation is crucial to prevent accidents and ensure compliance with safety standards.
Importance of Safety Measures
Proper safety measures protect workers and the public from electrical hazards. This includes using protective equipment and following protocols during installation.
Role of Signage
Signage plays a vital role in maintaining safety by clearly marking hazardous areas and underground installations. It alerts workers and the public to potential dangers.
Tips for Effective Communication
- Use Clear, Visible Signs: Ensure signs are easily readable and placed at strategic locations.
- Include Warning Symbols: Use universal symbols to convey hazards quickly.
- Regular Updates: Keep information current to reflect any changes in the site conditions.
Regulation 7: Regular Maintenance and Upgrades
Regular maintenance of underground power systems is essential to ensure reliability and safety.
Necessity of Ongoing Maintenance
Continuous maintenance helps identify potential issues before they become major problems. It ensures that systems operate efficiently, preventing unexpected outages and reducing repair costs.
Benefits of Timely Upgrades and Repairs
Timely upgrades improve system performance and incorporate the latest technology, enhancing energy efficiency. Regular repairs extend the lifespan of the infrastructure and maintain compliance with safety standards.
Advice on Scheduling Regular Check-Ups
- Set a Maintenance Schedule: Conduct inspections at least annually or as recommended by your local regulations.
- Document Findings: Keep detailed records of inspections and any maintenance performed.
- Hire Professionals: Use certified electricians to perform check-ups, ensuring adherence to AS/NZS 3000 standards.
Regular check-ups and proactive maintenance keep your underground power systems safe and efficient.
Ensuring Safe and Compliant Power Installations
Following these regulations is crucial to ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of underground power systems. Proper planning, the use of certified materials, and professional installation all contribute to a secure and compliant system.
Regular maintenance and timely upgrades further enhance the infrastructure’s performance and reliability. Implementing safety measures and clear signage ensures both workers and the public remain protected, while ongoing inspections prevent potential issues from escalating.
These steps collectively safeguard your investment and maintain the integrity of the power supply.
Trusting professionals for power installations guarantees that all work is completed to the highest standards. Certified electricians bring expertise and experience essential for navigating complex regulations and technical requirements.
For those in Sydney, contacting Sydney Level 2 Electricians can provide peace of mind and quality service. They specialise in expert Underground Service Lines, ensuring your project is handled with care and precision.
Reach out to Sydney Level 2 Electricians for reliable and expert assistance with your underground power needs.